Notes, from: “Making Musical Apps with Csound using libpd and csoundapi~” at the 2nd International Csound Conference October 25th-27th, 2013, in Boston.
Overview
For about five months in 2013-2104 I worked as a programmer with Boulanger Labs to develop an app called Muse, using the Leap Motion sensor. Leap Motion is a controller that detects hand movement. Boulanger Labs is a a startup founded by Dr. Richard Boulanger “Dr. B” – to design music apps working with students in the Electronic Production and Design (EPD) department at Berklee College of Music.
Dr. B. was asked by a former student, Brian Transeau (BT), to help develop a music app in conjunction with Leap Motion. The goal was to have something in stores for Christmas – about 2 months from the time we started. BT would design the app and we would code it.
What would the app do? It would let you to improvise music in real time by moving your hands in the air. You would select notes from parallel horizontal grids of cubes – a melody note from the top, a chord from the middle, and a bass note from the bottom. It would be be beautiful and evolving like “Bloom” by Eno and Chilvers.
Getting started
We bought Leap Motion sensors. We downloaded apps from the Airspace store to learn about the capabilities of the sensor.
One of our favorite apps is “Flocking”. It displays glowing flames to represent fingers. When you move your fingers it causes a school of fish to disperse.
Making prototypes
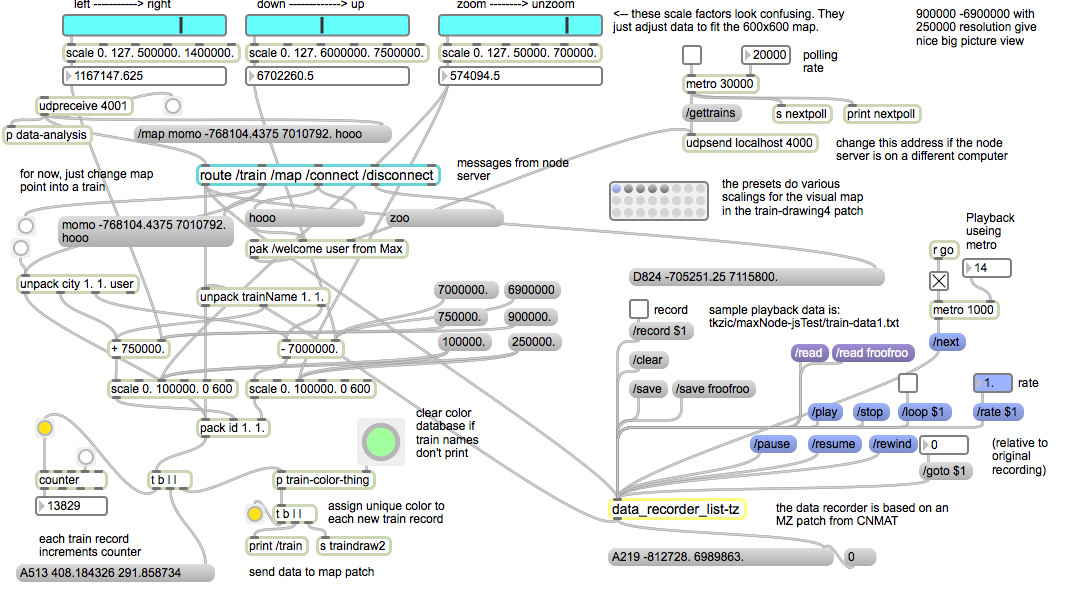
We started to make prototypes in Max, using the aka.leapmotion external.
This was the first prototype and one of my favorites. It randomly plays Midi notes in proportion to how you move your fingers. It feels responsive.
Mac Os app: https://reactivemusic.net/?p=7434
Max code: https://reactivemusic.net/?p=11727
Local file: leapfinger3.app (in Applications)
Does it remind you of any of this?
Design sketches from BT
“So this is an idea of the UI paralaxing. In the background it would be black with say stars. You could see your fingertips in this space and your hand movements would effect perspective changes in the UI. When you touch a cube it would light in 3D space radiating out (represented by the lens flares). This flare or light (like bloom) should continue in the direction you touched the cube. Instead of blocks, these would be grids *like 3D graph paper* subdivided into probably 12-24 cubes.”Best,_BT
Research:
Stephen Lamb joined the team as a C++ Open GL programmer, and began exploring the Leap Motion API in Cinder C++.
What kind of gestures can we get to work?
Darwin Grosse, of Cycling 74, sent us a new version of aka.leapmotion that handles predefined gestures, like swipes.
The next prototype was written, in CInder C++. An audio proof of concept. The FM oscillators and feedback delay are written at the sample level, using callbacks. The delay line code was borrowed from Julius O. Smith at CCRMA: https://reactivemusic.net/?p=7513
http://zerokidz.com/ideas/?p=8643
Delay line code: https://reactivemusic.net/?p=7513
Christopher Konopka, sound designer and programmer, joins the team, but won’t be able to work on the project until October.
At this point we are having doubts about the utility of the Leap Motion sensor for musical apps. Because it is camera-based, the positioning of hands is critical. There is no haptic feedback. We are experiencing high rates of false positives as well as untracked gestures.
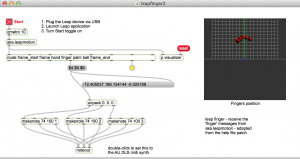
More prototypes in Max
- Finger painting
- Left right hand detection
- Detecting state changes
- Defining gestures (air piano)
http://zerokidz.com/ideas/?p=9448
http://zerokidz.com/ideas/?p=9485
Reactive Music
Dr. B asks us to consider RJDJ style environmental effects.
This is when we find out that audio input doesn’t work in Cinder. After staying up until about 6 AM, I decide to run a test of libPd in openFrameworks C++. It works within minutes. libPd allows Pd to run inside of C++. By the way, libPd is the platform used by RJDJ.
Programming notes:
Csound
We can now write music using Pd, and graphics using OpenGL C++. This changes everything.
What about Csound? It also runs in Pd. Will it run in libPd? Dr. B introduces me to Victor Lazarrini – author of csoundapi~ and we figure out how to compile Csound into the project that evening.
Paul Batchelor joins the team. He is writing generative music in Csound for a senior project at Berklee. Paul and Christopher write a Csound/Pd prototype, in a couple of days – that will form the musical foundation of the app.
We build a prototype using Paul’s generative Csound music and connect it in to Leap Motion in openFrameworks.
Local file: (leapPdTest5ExampleDebug.app in applications)
In this next video, it feels like we are actually making music.
Note: local source code is ofx8 addons leapmotion : leapPdTest5 – but it probably won’t compile because we moved the libs into the proper folders later on
Combining three prototypes:
This was a week of madness. We had essentially three separate apps that needed to be joined: Steve’s Open GL prototype, my libPd prototype, and Paul’s Csound code. So every time Steve changed the graphics – or Paul modified the Csound code – I needed to re-construct the project.
Finally we were able to upload a single branch of the code to Github.
Tweaking the architecture
Steven Yi, programmer and Csound author, helped repair the xCode linking process. We wanted to be able to install the App without asking users to install Csound or Pd. Steven Yi figures out how to do this in a few hours…
Later that day, for various reasons Steve Lamb leaves the project.
I take over the graphics coding – even through I don’t know OpenGL. BT is justifiably getting impatient. I am exhausted.
Redesigning the graphics
Jonathan Heppner, author of AudioGL, joins the team. Jonathan will redo the graphics and essentially take over the design and development of the app in collaboration with Dr. B.
There is an amazing set of conference calls between Leap Motion, BT, Dr.B, and the development team. Leap Motion gives us several design prototypes – to simplify the UI. Dr. B basically rules them out, and we end up going with a Rubik’s cube design suggested by Jonathan. At one point BT gives a classic explanation of isorhythmic overlapping drum loops.
While Jonathan is getting started with the new UI, We forked a version, to allow us to refine the Osc messaging in Pd.
Christopher develops an extensive control structure in Pd that integrates the OpenGL UI with the backend Csound engine.
Christopher and Paul design a series of sample sets, drawing from nature sounds, samples from BT, Csound effects, and organically generated Csound motif’s. The samples for each set need to be pitched and mastered so they will be compatible with each other.
At this point we move steadily forward – there were no more prototypes, except for experiments, like this one: http://zerokidz.com/ideas/?p=9135 (that did not go over well with the rest of the team :-))
Tom Shani, graphic designer, and Chelsea Southard, interactive media artist, join the team. Tom designs a Web page, screen layouts, logos and icons. Chelsea provides valuable user experience and user interface testing as well as producing video tutorials.
Also, due to NDA’s, development details from this point on are confidential.
We miss the Christmas deadline.
The NAMM show
That brings us up to the NAMM show where BT and Dr. B produce a promotional video and use the App for TV and movie soundtrack cues.
http://zerokidz.com/ideas/?p=9615
February
There are more than a few loose ends. The documentation and how-to videos have yet to be completed. There are design and usability issues remaining with the UI.
This has been one of the most exhausting and difficult development projects I have worked on. The pace was accelerated by a series of deadlines. None of the deadlines have been met – but we’re all still hanging in there, somehow. The development process has been chaotic – with flurries of last minute design changes and experiments preceding each of the deadlines. We are all wondering how Dr. B gets by without sleep?
I only hope we can work through the remaining details. The app now makes beautiful sounds and is amazingly robust for its complexity. I think that with simplification of the UI, it will evolve into a cool musical instrument.
In the app store
We scaled back features and added a few new ones including a control panel, a Midi controller interface, a new percussion engine, and sample transposition tweaks. With amazing effort from Christopher, Jonathan, Paul, Chelsea, Tom S., and Dr. B – the app is completed and released!
https://airspace.leapmotion.com/apps/muse/osx
But why did it get into the Daily Mail? http://www.dailymail.co.uk/sciencetech/article-2596906/Turn-Mac-MUSICAL-INSTRUMENT-App-USB-device-lets-use-hand-gestures-make-sounds.html