Notes:
Audio Signal Processing Course: https://www.coursera.org/course/audio
By Xavier Serra and Julius O. Smith
This is a free course offered by Stanford. It starts at the beginning of October. I will be taking the course and would be happy to help you if you are interested in taking it too.
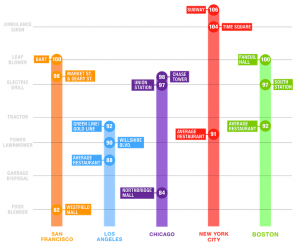
Pd weekend 2014: Katja Vetter Microphone design: http://libguides.lib.siu.edu/puredata
Part I – Pitch detection
How would you construct an ‘Autotune’ effect that works in real time? The first requirement is accurate pitch detection:
Frequency domain:
FFT and STFT: Find frequencies where the signal has greatest energy. Tradeoff between frequency and temporal resolution. Moderate latency.
Max examples: https://reactivemusic.net/?p=11202
Also look at the builtin Max tutorials on the fft~ and pfft~ objects
3rd party Max/Pd objects:
DSP code
Time domain:
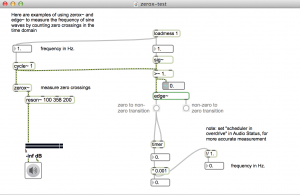
Zero crossing: Measure the period of waves by counting rate of zero crossings. Doesn’t work with complex waveforms.
Max objects: fzero~ and zerox~
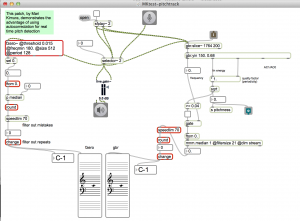
Autocorrelation: Compare a signal with a time shifted copy of itself. Low latency but CPU intensive. Can be improved by using lower sample rates and other tweaks. (Helmholtz)
Example patches: https://reactivemusic.net/?p=17169
(note: gbr.yin~ is a 3rd party object from IRCAM, but is built into Max)
Pd examples from Katja Vetter: (helmholtz~ external)
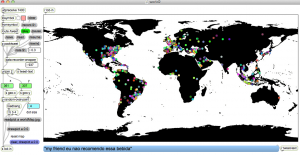
We also looked at Katja’s new app: InstantDecomposer. If you would like to try this patch, please contact me. I will need to get permission from Katja.
Wavelet transform:
Other methods:
- phase locked loop
- human pitch matching (what is the latency?)
- Neural networks?
- Statistical methods (pattern matching)?
Part II – Prototyping
Muse development case study: https://reactivemusic.net/?p=16187
Assignment
Next week we will listen to your music from the future.