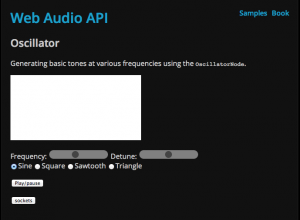
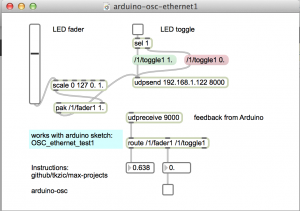
Bi-directional communication from touchOSC to Arduino using an ethernet shield.
In this version, the Macbook is directly connected to the Arduino to provide a serial monitor for status updates.
How it works: press a toggle, or move a fader, in touchOSC – it sends a message to the Arduino which lights up, or fades, an LED – then sends back an OSC message to touchOSC to light up the toggle button. (note: local feedback should be off for the toggle button in touchOSC. This is the default)
Arduino circuit
- Use an ethernet shield.
- Connect ethernet cable. (I am using a Netgear WNCE2001 ethernet to wiFi adapter)
- LED is connected to pin 5 and ground. The shorter lead connects to ground.
Instructions
- Connect Arduino to Macbook via USB.
- Open the Arduino serial monitor to initialize the ethernet connection and display the IP address.
touchOSC
- In touchOSC or Max, set the target IP to the one just displayed in the Arduino serial monitor
- From touchOSC (or Max) send on port 8000, receive on port 9000.
- Use the default touchOSC layout (simple)
- Use /fader1 and /toggle1 to control the LED
Max
- Open arduino-osc-ethernet1.maxpat
- Set ip address in [udpsend] to the one just displayed in the Arduino serial monitor
- Have some fun
Fixed IP address
update 1/2016: A version of the Arduino sketch that uses a fixed IP instead of DHCP is located in the folder: OSC_ethernet_fixedIP/
The IP is set to 192.168.1.177 but you can change it to any valid address on your network.
Arduino sketch
// generic Arduino OSC program
// works from Max or touchOSC
//
// plug LED into pin 5 (and gnd)
//
// requires ethernet shield
//
// use serial monitor to get the ip address
//
// use these OSC commands (will work from first page of touchOSC simple layout
//
// /1/fader1
// /1/toggle1
//
#include <SPI.h>
#include <Ethernet.h>
#include <ArdOSC.h>
byte mac[] = { 0x90, 0xA2, 0xDA, 0x0D, 0x0B, 0xCE }; //physical mac address
OSCServer server;
OSCClient client;
int serverPort = 8000; //Touch OSC Port (outgoing)
int destPort = 9000; //Touch OSC Port (incoming)
int ledPin = 5;
int flag=0;
void setup(){
pinMode(2, OUTPUT);
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println("DNS and DHCP-based OSC server");
// start the Ethernet connection:
if (Ethernet.begin(mac) == 0) {
Serial.println("Failed to configure Ethernet using DHCP");
// no point in carrying on, so do nothing forevermore:
while(true);
}
// print your local IP address:
Serial.print("Arduino IP address: ");
for (byte thisByte = 0; thisByte < 4; thisByte++) {
// print the value of each byte of the IP address:
Serial.print(Ethernet.localIP()[thisByte], DEC);
Serial.print(".");
}
Serial.println();
Serial.println();
//start the OSCserver
server.begin(serverPort);
//add OSC callback function. One function is needed for every TouchOSC interface element that is to send/receive OSC commands.
server.addCallback("/1/toggle1", &funcOnOff);
server.addCallback("/1/fader1", &funcFader);
}
void loop(){
if(server.aviableCheck()>0){
// Serial.println("alive! ");
}
}
//When the button on the TouchOSC inteface is pressed, a message is sent from the iDevice
//to the Arduino to switch (togle) the LED on the Arduino on/off
//then a messeage is sent bak from the Arduino to the iDevice to toggle the buttom on/off
void funcOnOff(OSCMessage *_mes){
float value = _mes->getArgFloat(0); //TouchOSC expects float values
//create new osc message
OSCMessage newMes;
//set destination ip address & port no
newMes.setAddress(_mes->getIpAddress(),destPort);
newMes.beginMessage("/1/toggle1");
Serial.println(value);
if(value < 1.0) {
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW);
}
else{
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH);
}
newMes.addArgFloat(value);
//send osc message
//
// turn local feedback off on touch-osc control to test this
client.send(&newMes);
}
// new callback for fader - using same comments
//When the button on the TouchOSC inteface is pressed, a message is sent from the iDevice
//to the Arduino to switch (togle) the LED on the Arduino on/off
//then a messeage is sent bak from the Arduino to the iDevice to toggle the buttom on/off
void funcFader(OSCMessage *_mes){
float value = _mes->getArgFloat(0); //TouchOSC expects float values
//create new osc message
OSCMessage newMes;
//set destination ip address & port no
newMes.setAddress(_mes->getIpAddress(),destPort);
newMes.beginMessage("/1/fader1");
Serial.println(value);
int ledValue = value * 255.0;
analogWrite(ledPin, ledValue);
newMes.addArgFloat(value);
//send osc message
//
// turn local feedback off on touch-osc control to test this
client.send(&newMes);
}