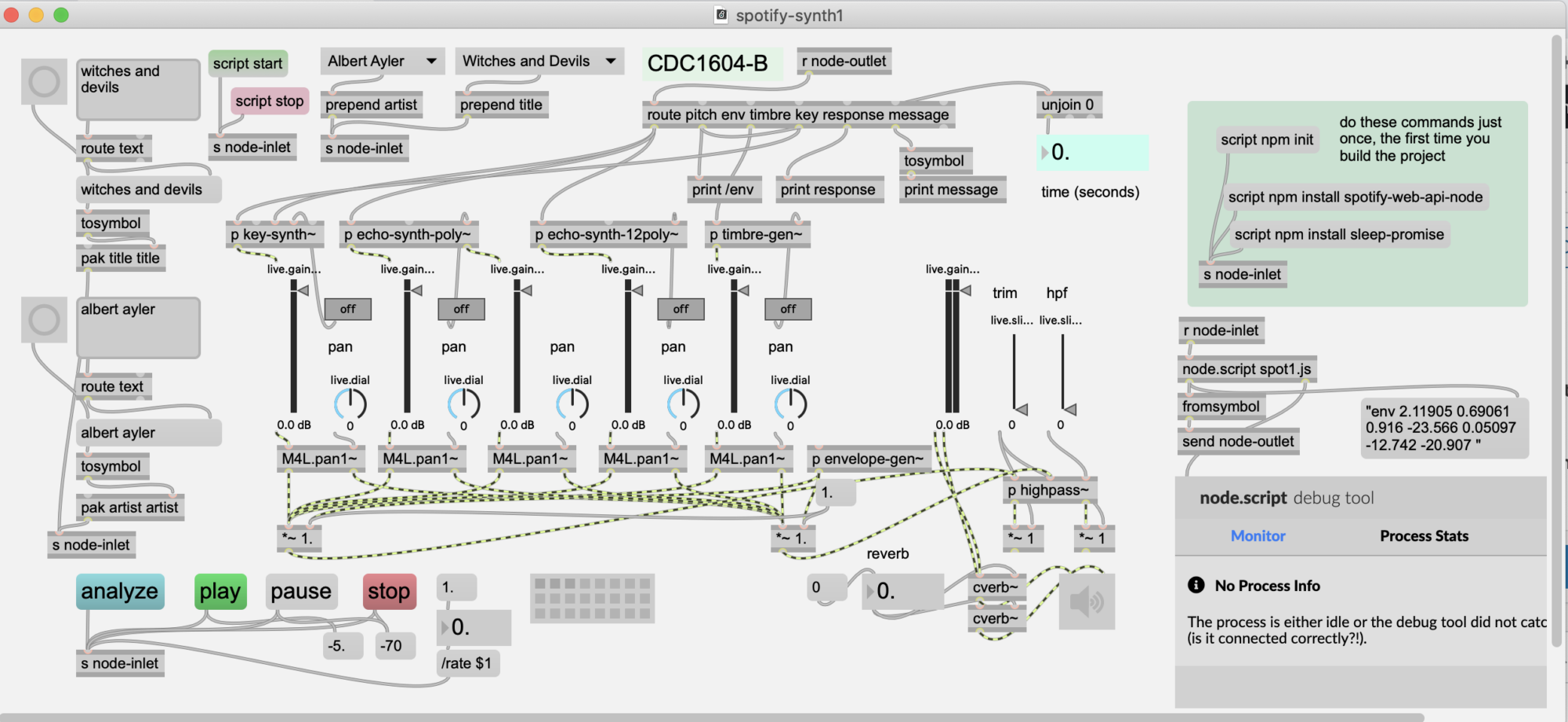
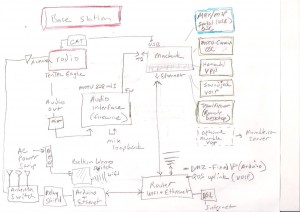
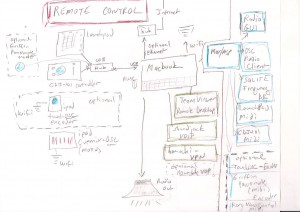
With a TenTec Eagle transceiver, Managed by N4PY software.
N4PY acts as router, distributing CAT commands to other applications.
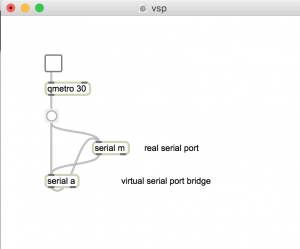
The applications are connected using virtual serial port bridge pairs. For each of the applications, N4PY emulates a K3 transceiver on one side of the bridge.
- Panadapter: NAP3
- Logger: N1MM
- CW Skimmer
The CW keyer is a K1EL Winkeyer USB controlled solely by the N1MM logger.
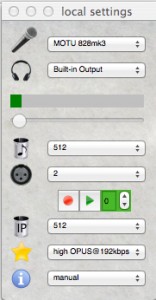
The routing of IQ signals from LP-PAN2 SDR is done through a MOTU 828 mk3 interface, simply to be able to split the signal so that both NAP3 and CW Skimmer can use it.
CW Skimmer gets the IQ signal directly from the MOTU. NAP3 doesn’t not recognize multiple ports on soundcards. So one end of the split from the MOTU is sent through another audio interface (Focusrite 2I2). NAP3 uses the 2I2 as an input device.
LP-PAN frequency adjustments
Notes on configuration for correct zero-beating.
When setting the Eagle BW or PBT, the IF will shift in frequency, so the numbers below assume a centered PBT and a BW of 700.
The sidetone pitch is 523 Hz.
Settings may also depend on which roofing filters are installed in the Eagle.
NAP3 settings
Set the global offset to -8200. Leave everything else at 0.
CW Skimmer settings
- CW pitch: 523
- Audio IF: -7520
- Sample rate: 96 kHz
- Hardware: SoftRock-IF
This post is about ham radio.