Update: 5/2014
Retrying this experiment using the Arduino circuit described here: https://reactivemusic.net/?p=12161
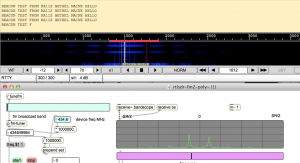
notes
- 300 baud
- 300 Hz carrier shift
- 8 bits
- 2 stop
- no parity
- filter at 300 Hz
- Normal mode (not reverse)
- AFC on
There are 2 programs:
- serial.c – sends a beacon then transmits a 640×480 picture
- serial-beacon.c – just sends a beacon
In order to view the picture as it comes in in dl-fldigi, you need to open up the SSDV RX window in the View menu.
The frequency is not very stable and occasionally you need to just restart dl-fldigi because the screen fills with trash characters.
Also, in Max, you need to tune on the right half of the picture.
—
Will be setting up a test with smaller photos
Success: Got an accurate beacon at 300 baud today and send a jpeg picture file , taken by a webcam connected to the R-Pi using fswebcam and SSDV.
http://www.slblabs.com/2012/09/26/rpi-webcam-stream/
Used the same circuit as the previous post about the Arduino RTTY beacon.
The difference is that we’re using a C program to write the text directly to the serial port which modulates the NTX2 transmit frequency.
Transmission can be stopped and started using the sleep() function but the timing is not exact.
Local code
tkzic/rpi/serial/serial1 –
- using command line SSDV converter in tkzic/rpi/ssdv-master.
- Using dl-fldigi to decode RTTY and SSDV pictures.
- Using logictech c210 webcam – see link above for how to take a picture and save to file use fswebcam.
[Todo:]
- Set up a shell script to take pictures and transmit regular intervals.
- upload code and photos
- Build some antennas
- Field test
- Buy a balloon




