Translates back and forth from English to Japanese seeking equilibrium.
Review of speech synthesis technology
By Sami Lemmetty at University of Helsinki, 1999
http://research.spa.aalto.fi/publications/theses/lemmetty_mst/index.html
Includes links to Speech synthesis demonstration CD http://research.spa.aalto.fi/publications/theses/lemmetty_mst/appa.html
Warping acapella tracks
In Ableton Live
By Thavius Beck at Dubspot
Vocaloid tutorial
by soundwavescience
Hearing voices
A presentation for Berklee BTOT 2015 http://www.berklee.edu/faculty
(KITT dashboard by Dave Metlesits)
The voice was the first musical instrument. Humans are not the only source of musical voices. Machines have voices. Animals too.
Topics
- synthesizing voices (formant synthesis, text to speech, Vocaloid)
- processing voices (pitch-shifting, time-stretching, vocoding, filtering, harmonizing),
- voices of the natural world
- fictional languages and animals
- accents
- speech and music recognition
- processing voices as pictures
- removing music from speech
- removing voices
Voices

We instantly recognize people and animals by their voices. As an artist we work to develop our own voice. Voices contain information beyond words. Think of R2D2 or Chewbacca.
There is also information between words: “Palin Biden Silences” David Tinapple, 2008: http://vimeo.com/38876967
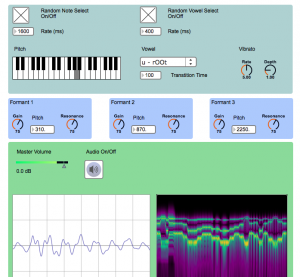
Synthesizing voices
The vocal spectrum
What’s in a voice?
- Formant synthesis in Max by Mark Durham: https://reactivemusic.net/?p=9294 (singing vowels with formants)
- Formant synthesis Tutorial by Jordan Smith: https://reactivemusic.net/?p=9290 (making consonants with noise)
Singing chords
Humans acting like synthesizers.
- Singing chords: Lalah Hathaway https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=c5AdOZtRdfE (0:30)
- Tuvan throat singing: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5wHbIWH_NGc (near the end of the video)
- Polyphonic overtone singing: Anna-Maria Hefele https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vC9Qh709gas
More about formants
- Formants (Wikipedia) http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Formant
- Rooms have resonances: “I am sitting in a Room” by Alvin Lucier
- Singer’s formant (2800-3400Hz).
Text to speech
Teaching machines to talk.
- phonemes (unit of sound)
- diphones (combination of phonemes) (Mac OS “Macintalk 3 pro”)
- morphemes (unit of meaning)
- prosody (musical quality of speech)
Methods
- articulatory (anatomical model)
- formant (additive synthesis) (speak and spell)
- concatentative (building blocks) (Mac Os)
Try the ‘say’ command (in Mac OS terminal), for example: say hello
More about text to speech
- History of speech synthesis http://research.spa.aalto.fi/publications/theses/lemmetty_mst/chap5.html (Helsinki University of Technology 1999)
- Speech synthesizers, 2014 https://reactivemusic.net/?p=18141
- Speech synthesis web API https://reactivemusic.net/?p=18138
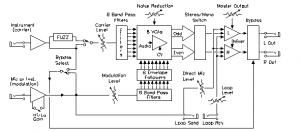
Vocoders
Combining the energy of voice with musical instruments (convolution)
- Peter Frampton “talkbox”: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EqYDQPN_nXQ (about 5:42) – Where is the exciting audience noise in this video?
- Ableton Live example: Local file: Max/MSP: examples/effects/classic-vocoder-folder/classic_vocoder.maxpat
- Max vocoder tutorial (In the frequency domain), by dude837 – Sam Tarakajian https://reactivemusic.net/?p=17362 (local file: dude837/4-vocoder/robot-master.maxpat
More about vocoders
- How vocoders work, by Craig Anderton: https://reactivemusic.net/?p=17218
- Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vocoder. Engineers conserving information to reduce bandwith
- Heterodyne filter: https://reactivemusic.net/?p=17338 – digital emulation of an analog filter bank.
- Max/MSP: examples/effects/classic-vocoder-folder/classic_vocoder.maxpat
Vocaloid
By Yamaha
(text + notation = singing)
- Vocaloid website: http://www.vocaloid.com/en/
- Hatsune Miku: https://reactivemusic.net/?p=6891
Demo tracks: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QWkHypp3kuQ
- Vocaloid tutorial
- #1 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vcJDTDBWTrw (entering notes and lyrics – 1:25)
- #2 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qpGwgIyMGOk (raw sound – 0:42)
- #5 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YEAuL6Q2j-0 (with phrasing, vibrato, etc.,- 1:00)
Vocaloop device http://vocaloop.jp/ demo: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xLpX2M7I6og#t=24
Processing voices
Transformation
Pitch transposing a baby https://reactivemusic.net/?p=2458
Real time pitch shifting
Autotune: “T-Pain effect” ,(I-am-T-Pain bySmule), “Lollipop” by Lil’ Wayne. “Woods” by Bon Iver https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1_cePGP6lbU
Autotuna in Max 7
by Matthew Davidson
Local file: max-teaching-examples/autotuna-test.maxpat
InstantDecomposer in Pure Data (Pd)
by Katja Vetter
http://www.katjaas.nl/slicejockey/slicejockey.html
Autocorrelation: (helmholtz~ Pd external) “Helmholtz finds the pitch” http://www.katjaas.nl/helmholtz/helmholtz.html
(^^ is input pitch, preset #9 is normal)
- local file: InstantDecomposer version: tkzic/pdweekend2014/IDecTouch/IDecTouch.pd
- local file: slicejockey2test2/slicejockey2test2.pd
Phasors and Granular synthesis
Disassembling time into very small pieces
- sorting noise; http://youtu.be/kPRA0W1kECg
- Phasors: https://reactivemusic.net/?p=17353
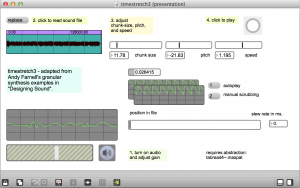
Time-stretching
Adapted from Andy Farnell, “Designing Sound”
https://reactivemusic.net/?p=11385 Download these patches from: https://github.com/tkzic/max-projects folder: granular-timestretch
- Basic granular synthesis: graintest3.maxpat
- Time-stretching: timestretch5.maxpat
More about phasors and granular synthesis
- Shepard tone upward glissando by Chris Dobrian: https://reactivemusic.net/?p=17255
- “Falling Falling” (Visual Shepard tone) https://reactivemusic.net/?p=17251
- Ableton Live – granulator (Robert Henke)
Phase vocoder
…coming soon
Sonographic sound processing
Changing sound into pictures and back into sound
by Tadej Droljc
https://reactivemusic.net/?p=16887
(Example of 3d speech processing at 4:12)
local file: SSP-dissertation/4 – Max/MSP/Jitter Patch of PV With Spectrogram as a Spectral Data Storage and User Interface/basic_patch.maxpat
Try recording a short passage, then set bound mode to 4, and click autorotate
Speech to text
Understanding the meaning of speech
The Google Speech API
A conversation with a robot in Max
https://reactivemusic.net/?p=9834
Google speech uses neural networks, statistics, and large quantities of data.
More about speech to text
- Real time German/English translator (Microsoft) http://digg.com/video/heres-microsoft-demoing-their-breakthrough-in-real-time-translated-conversation
- Skype translator – Spanish/English: http://www.skype.com/en/translator-preview/
- Dragon Naturally Speaking (Nuance) accidentally converts music to poetry
Voices of the natural world
Changes in the environment reflected by sound
- Bernie Krause: “Soundscapes”
Fictional languages and animals
“You can talk to the animals…”
- Derek Abbot’s animal noise page: http://www.eleceng.adelaide.edu.au/Personal/dabbott/animal.html
- Quack project http://www.quack-project.com/table.cgi
- Fictional language dialog by Naila Burney: https://reactivemusic.net/?p=7242
Pig creatures example: http://vimeo.com/64543087
- 0:00 Neutral
- 0:32 Single morphemes – neutral mode
- 0:37 Series, with unifying sounds and breaths
- 1:02 Neutral, layered
- 1:12 Sad
- 1:26 Angry
- 1:44 More Angry
- 2:11 Happy
What about Jar Jar Binks?
Accents
The sound changes but the words remain the same.
The Speech accent archive https://reactivemusic.net/?p=9436
Finding and removing music in speech
We are always singing.
Jamming with speech
- Drummer jams with a speed-talking auctioneer: https://reactivemusic.net/?p=7140
- Guitarist imitates crying politician: http://digg.com/video/guitarist-plays-along-to-sobbing-japanese-politician
Removing music from speech
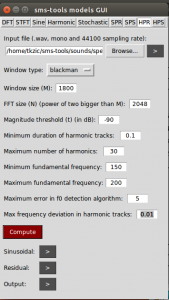
SMS-tools
by Xavier Serra and UPF
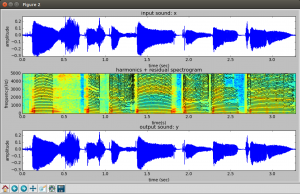
Harmonic Model Plus Residual (HPR) – Build a spectrogram using STFT, then identify where there is strong correlation to a tonal harmonic structure (music). This is the harmonic model of the sound. Subtract it from the original spectrogram to get the residual (noise).
Settings for above example:
- Window size: 1800 (SR / f0 * lobeWidth) 44100 / 200 * 8 = 1764
- FFT size: 2048
- Mag threshold: -90
- Max harmonics: 30
- f0 min: 150
- f0 max: 200
feature detection
- time dependent
- Low level features: harmonicity, amplitude, fundamental frequency
- high level features: mood, genre, danceability
Acoustic Brainz: (typical analysis page) https://reactivemusic.net/?p=17641
Essentia (open source feature detection tools) https://github.com/MTG/essentia
Freesound (vast library of sounds): https://www.freesound.org – look at “similar sounds”
Removing voices from music
A sad thought
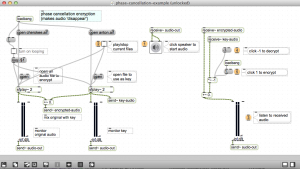
phase cancellation encryption
This method was used to send secret messages during world war 2. Its now used in cell phones to get rid of echo. Its also used in noise canceling headphones.
https://reactivemusic.net/?p=8879
max-projects/phase-cancellation/phase-cancellation-example.maxpat
Center channel subtraction
What is not left and not right?
Ableton Live – utility/difference device: https://reactivemusic.net/?p=1498 (Allison Krause example)
Local file: Ableton-teaching-examples/vocal-eliminator
More experiments
- Synthesizing laughter
- Bobby McFerrin: (pentatonic scale) http://www.ted.com/talks/bobby_mcferrin_hacks_your_brain_with_music.html
- Alphabet vocals
- jii lighter https://reactivemusic.net/?p=6970
- Sesame St – Joan LaBarbara: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=y819U6jBDog
- Warping acapella tracks https://reactivemusic.net/?p=18046
Questions
- Why do most people not like the recorded sound of their voice?
- Can voice be used as a controller?
- (Imitone: http://imitone.com)
- Mari Kimura
- How do you recognize voices?
- Does speech recognition work with singing?
- How does the Google Speech API know the difference between music and speech?
- How can we listen to ultrasonic animal sounds?
- What about animal translators?
A vocoder in Max
In the frequency domain
By Dude837
download
http://www.otherbirds.com/tutorials/4-vocoder.zip
All tutorials: http://www.otherbirds.com/tutorials
Third octave filtering
Using the fffb~ object in Max – with feedback and vocoder effects.
By Peter Elsea
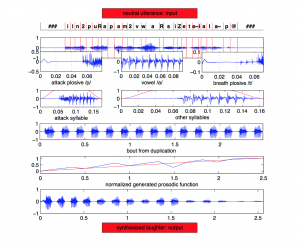
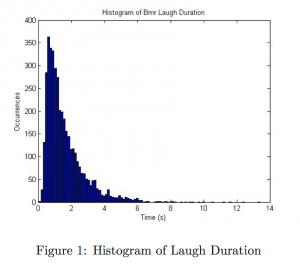
Laughter synthesis
Semi-Parametric Synthesis of Speaker-Like Laughter
By Greg Beller at IRCAM, 2008
http://www.gregbeller.com/2008/06/laughter-synthesis/
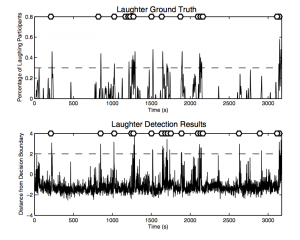
Automatic laughter detection
a system to automatically detect laughter from acoustic features of audio using neural networks.
By Mary Knox at Berkeley
https://www.icsi.berkeley.edu/pubs/speech/laughter_v10.pdf
Laughter detection in meetings
A system to automatically detect laughter events.
By Lyndon S. Kennedy and Daniel P.W. Ellis at Columbia University and ICSI
http://www.ee.columbia.edu/~lyndon/pubs/nistrt2004-laughter.pdf