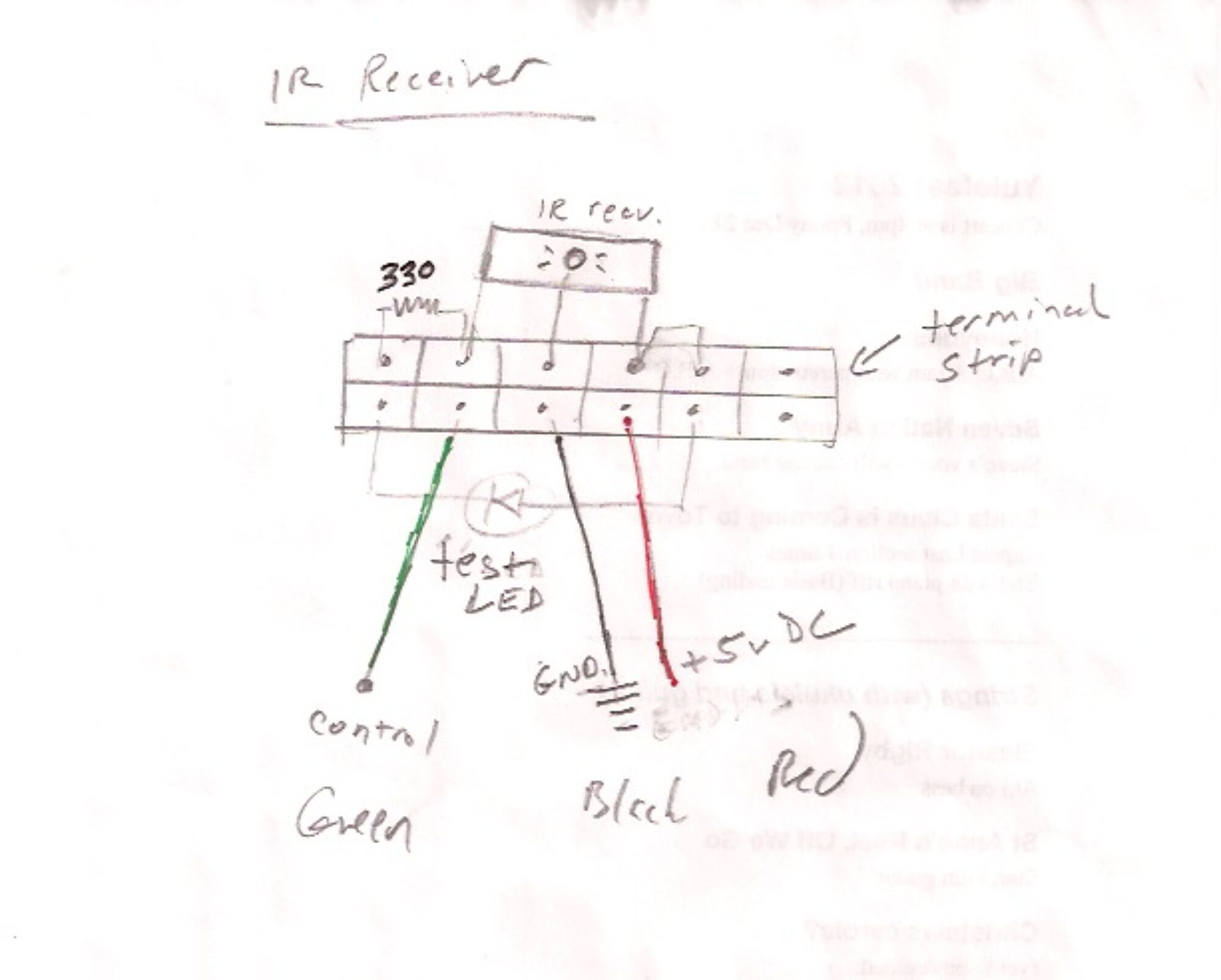
Draw points in Max by sending latitude and longitude to a Web client via Osc and web sockets.
Uses Ruby, WebSockets, Chrome, Google Maps API, Osc, Max, Jquery, and Node.js… But the Max patch is actually quite simple.
Based on this geocoding tutorial: http://www.sitepoint.com/google-maps-api-jquery/
download
https://github.com/tkzic/internet-sensors
folder: google-maps
files
main Max patch
- googlemaptest.maxpat
html and javascript for Google API
- js/ (folder containing javascript code for map client)
- markers.html (web client)
- mapserver.rb (Osc and Websockets server)
node.js (optional)
- nodeserver.js (local node.js webserver)
running node.js local web server (optional)
To run the project locally, you will either need to install node.js or have a local web server. The instructions assume that you have installed node, as well as the http package.
If you don’t want to bother with node, there is also an online version of the web client running at http://zerokidz.com/gmap/markers/markers.html
intalling ruby gems
Running Ruby 2.0 as well as the following gems:
- osc-ruby
- em-websocket
- json
instructions
1. If you are using the online Web client, go to this URL in a Google Chrome browser: http://zerokidz.com/gmap/markers/markers.html then skip to step 4.
2. In a terminal window start the node webserver
node nodeserver
3. Launch a Google Chrome web browser and type in this URL
127.0.0.1:8081/markers.html
4. In another terminal window start the ruby server for Osc and websockets
ruby mapserver.rb
5. Now in the Web Client (Chrome) press the “OSC” button underneath the map – to open the web sockets connection with the ruby server.
6. Open the Max patch:
googlemaptest.maxpat
7. Now you should be able to click on the message boxes for Bethel and Rumford in the Max patch to add location markers to the map in the browser.